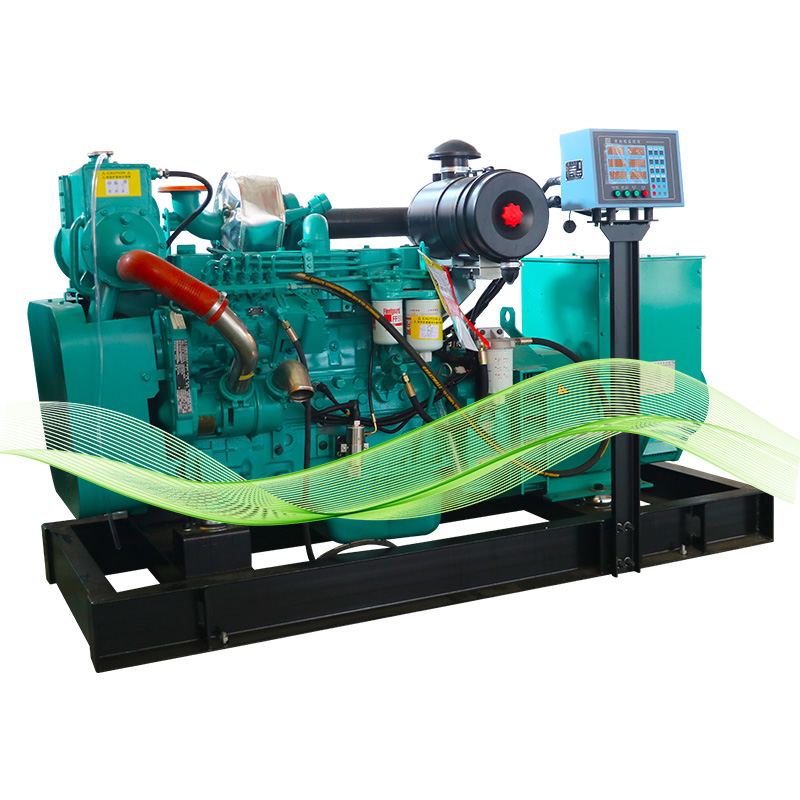
Key Differences Between Diesel and Gas Generators
How Diesel and Gas Generators Work
The way diesel and gas generators work is pretty different when it comes to making electricity. Diesel engines basically compress fuel until it ignites, turning chemical energy first into mechanical motion and then into electrical current. Gas generators take another approach altogether, using spark plugs to light the fuel mixture. While this method starts things going faster, it doesn't burn as efficiently as diesel does. Because of this difference in combustion, diesel generators tend to produce more power and maintain better efficiency even when loads change throughout the day. For instance, a diesel engine typically delivers about double what a similarly sized gas generator would put out thanks to how much energy is packed into diesel fuel. Looking at actual numbers from various industry sources, we see that most diesel generators run at around 40% efficiency while their gas counterparts usually manage only about 30%. These differences matter a lot for businesses deciding which type makes sense for their operations.
Fuel Types and Storage Requirements
What kind of fuel powers a generator makes a big difference in how it runs and what people need to think about when using it. Most diesel generators run on regular diesel fuel, though some folks are turning to biodiesel as a greener option these days. Gas powered units work with either natural gas or regular gasoline instead. The cost side of things shows diesel tends to be cheaper at first glance, but prices swing around quite a bit depending on the market situation. Natural gas usually costs less overall and stays pretty consistent in price. Storing these fuels presents different challenges too. Diesel actually lasts longer since it doesn't evaporate as quickly, so proper storage containers are still important even though it's not as dangerous as other options. Gasoline tells a different story entirely though. Because it's so much more flammable, anyone keeping gas needs to follow strict safety rules all the time. From what we see in practice, good quality diesel stored properly can sit around for about a year before it starts going bad. Gasoline just doesn't last nearly that long without losing effectiveness, which means users have to plan refills more frequently if they want their equipment to perform right.
Typical Applications for Each Type
When deciding between diesel and gas powered generators, most people look at what they actually need for their situation since each type has its own strengths. Diesel units tend to be the go to option for big jobs like construction sites, powering equipment in remote locations, or running entire factories because they just plain work better when reliability matters most and when there's a need for serious power output. Gas generators meanwhile make more sense for homes or smaller portable needs, especially where noise levels matter and folks want something that doesn't pollute as much. We've seen diesel generators keep hospitals running during outages and power massive earth moving machines on mining operations. On the flip side, many newer developments focus on green energy solutions where gas generators fit right in thanks to their lower emission profile. With regulations getting tighter around carbon footprints, more businesses are starting to see value in switching over to these cleaner burning alternatives even if it means paying a bit extra upfront.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Power Output and Runtime Differences
Picking between diesel and gas generators really comes down to knowing how much power they can deliver and how long they'll run before needing refueling. Most folks know that diesel engines pack a bigger punch than their gas counterparts, which makes them ideal for tough jobs where reliability matters most. Take a look at what happens during normal operation too – diesel units often last longer when working hard because they burn fuel more efficiently. That's why many boats rely on diesel power sources, as well as big industrial sites that need constant electricity supply without interruption. Gas powered models work better for situations where people need to adjust power levels quickly though. They just don't match up to diesel when it comes to maximum output or keeping going for extended periods. So if someone wants to select the best option for their particular situation, they should think carefully about exactly what kind of power demands exist and whether those demands will change over time.
Fuel Efficiency Metrics for Electric Generators
When looking at electric generators, how much fuel they burn matters a lot because it affects running expenses and what we put into the environment. Diesel models tend to get better mileage than their gas counterparts, burning fewer gallons per kilowatt hour produced. Sure, diesel fuel costs more initially, but those savings pile up over months and years of operation. Studies show load management makes all the difference here. Diesel units can handle different workloads without dropping efficiency too much. Most professionals suggest matching generator size to actual needs and managing loads carefully to squeeze out maximum efficiency from these machines. On the flip side, natural gas generators come with cheaper fuel prices right off the bat. They also perform better in situations where power demand keeps changing throughout the day. This means businesses should really take stock of their daily operations before making a choice between diesel and gas options.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
When picking out a generator, folks really need to think about how it affects the environment and what kind of emissions it produces because of all those regulations and sustainability stuff we hear so much about these days. Diesel generators tend to spew out way more nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and carbon than their gas counterparts. And this matters a lot since poor air quality can actually hurt people's health over time. The EPA has gotten pretty strict about limiting diesel generator usage lately to protect our planet from further damage. Gas generators just don't pollute as badly, making them look like the better choice when looking at environmental rules. We're seeing more companies go for hybrid setups or other green tech solutions too. These newer systems come equipped with parts designed specifically to cut down on emissions. Picking between different generator options means weighing environmental factors against what actually works operationally while staying within legal boundaries.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance Requirements
Initial Purchase vs Long-Term Fuel Costs
The price tag for diesel versus gas generators depends on things like how much power they produce and which manufacturer made them. Diesel units tend to cost more when bought new because they're built tougher and last longer in general. Fuel expenses for running diesel generators do run up higher than for gas models, but these machines usually get better mileage from what they burn. Looking at market trends, diesel fuel seems to be climbing in price slower than natural gas prices have been doing lately, so diesel might actually save money down the road despite those higher first costs. Anyone shopping around should really look at all the numbers together though not just what something costs to buy initially but also what it eats up month after month if they want to know whether their money will grow back through savings eventually.
Maintenance Complexity for Portable Gas Generators
The maintenance needs of diesel versus gas generators aren't really the same at all. Diesel units tend to need service less often, though when they do, the work tends to cost more because their components are so complicated. Regular stuff like changing oil, swapping out filters, and those big annual checkups are part of keeping them running smoothly. Gas powered models tell a different story though. They usually need attention more frequently even though their inner workings aren't as intricate. This means ongoing expenses for many businesses. Looking at real world data, diesel machines stand out for lasting longer thanks to consistent maintenance schedules and parts that most shops carry in stock. This makes a real difference when companies plan their maintenance budgets over time.
Durability and Lifespan Expectations
When it comes to lasting power, diesel generators tend to outlive their gas counterparts because they're built tougher and have simpler mechanical designs. Most diesel models will run for around 20,000 hours if maintained properly, whereas gas generators usually clock in somewhere between 10k and 15k hours before needing replacement. How long these machines actually last depends heavily on where they're installed, how frequently they operate, and naturally the quality of materials used in manufacturing. The warranty coverage for diesel units is usually much better too, which makes sense given all the field data showing they hold up over time. For businesses running heavy equipment operations where downtime costs money, investing in a diesel generator makes real sense since they just plain last longer under tough conditions.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Project
Matching Load Requirements to Generator Capacity
Getting the right generator starts with figuring out what kind of load it needs to handle versus what the generator can actually deliver. When looking at load requirements, first determine how many watts will be needed overall for whatever application this is going for. Think about both the maximum demand when everything kicks on at once and the regular day-to-day usage too. Picking something that matches those numbers makes all the difference. If the generator isn't big enough, things might not work properly or worse yet, could cause some serious damage over time. On the flip side, going way overboard just wastes money and burns through fuel faster than necessary. A good idea is to make a simple list covering important specs like volts, hertz rate, and whether single phase or three phase power is required. Most folks who know their stuff will tell anyone listening that getting the load specs right from the beginning saves headaches down the road.
Climate and Operational Environment Factors
The climate where a generator operates makes all the difference when it comes to performance and selection criteria. Extreme heat or cold, along with high humidity levels, really takes a toll on engine efficiency over time. For instance, in regions that regularly experience scorching temperatures, diesel models tend to hold up better because they're built tougher. Gas powered units work just fine in colder environments though, since they run smoother when temps drop. Beyond weather considerations, local noise ordinances and whether equipment can actually reach certain locations matter too. Portable options shine in places where loud operation is restricted by law. Many field technicians will tell stories about diesel generators keeping critical systems running during storms or power outages when everything else fails.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Regulatory compliance matters a lot when picking out generators, particularly since diesel and gas models face tough emissions and safety rules these days. Every country has its own set of regulations regarding what counts as acceptable emissions levels, and getting caught violating them can cost businesses thousands in fines plus all sorts of legal headaches. Just look at some recent cases where companies got hit with penalties because their generators didn't meet air quality requirements. Before setting up any generator operation, it pays to know exactly what permits are needed locally to stay on the right side of the law. Staying compliant protects not just the equipment itself but also keeps operations running smoothly according to both local ordinances and broader international standards that many industries now follow closely.