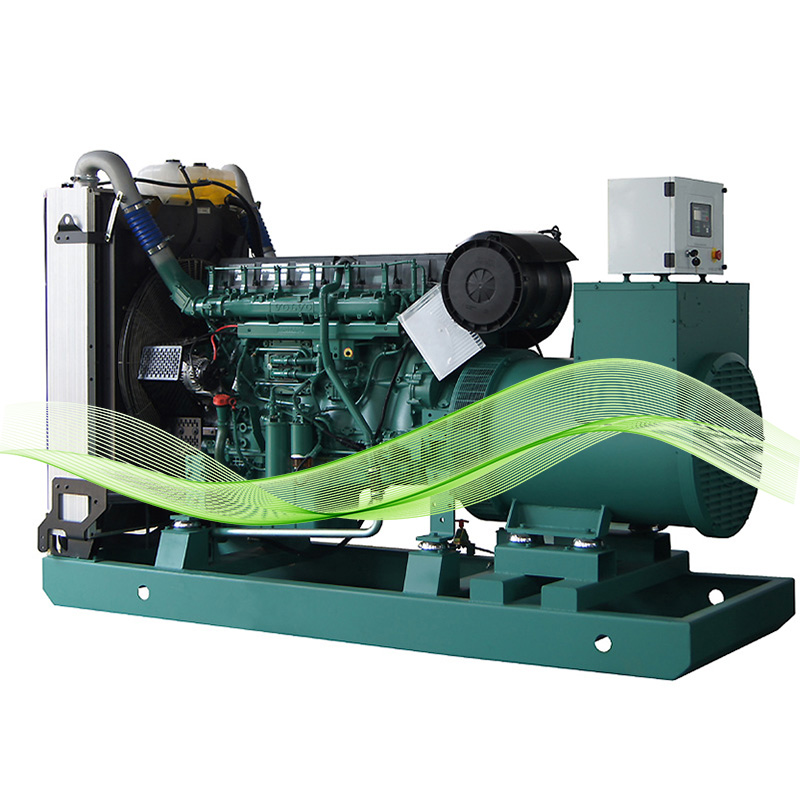
Რა არის ენერგეტიკული ეფექტიანობა გენერატორულ აგრეგატებში?
Როდესაც ვსაუბრობთ გაზის ელექტროგენერატორებზე, ენერგეტიკული ეფექტურობა ძირეულად მიუთითებს იმაზე, თუ რამდენად კარგად გადაიქცევა საწვავი გამოყენებად ელექტროენერგიად. ბევრი ფაქტორი მოქმედებს ამ ეფექტურობის მაჩვენებელზე, თუმცა ყველაფერი იწყება გენერატორის ძრავის კონსტრუქციით, მაგრამ მნიშვნელოვნად ასევე დამოკიდებულია ყოველდღიურ ექსპლუატაციაზე და რეგულარულ მოვლა-პოვლაზე. მარტივი საწვავის ხარჯის მაჩვენებლები არ აღწერს მთელ სურათს. რეალური სამუშაო პირობები ძალიან მნიშვნელოვანია – არ შეიძლება იგნორირდეს ის ფაქტორები, როგორიცაა გენერატორის მუშაობა სრული სიმძლავრის ქვემოთ, გარე ტემპერატურის ცვლილებები ან კიდევ იმ საწვავის ტიპი, რომლის წვაც ხდება. ამიტომ ახალგაზრდა ბუნებრივი გაზის გენერატორების მოდელები უკეთ ასრულებენ დღესდღეობით: ისინი იყენებენ ისეთ ტექნოლოგიებს, როგორიცაა ღია სისტემის წვა (lean burn) და გაუმჯობესებული გაგრილების მექანიზმები, რომლებიც მინიმალურად შეამცირებენ სითბოს დანაკარგს ოპერაციის დროს.
Ეფექტურობის გაზომვა: თერმული ეფექტურობა და საწვავიდან ელექტროენერგიის გარდაქმნა
Ორი ძირეული მაჩვენებელი განსაზღვრავს გაზის გენერატორის ეფექტურობას:
| Მეტრი | Განმარტება | Სამრეწველო სტანდარტული დიაპაზონი |
|---|---|---|
| Თერმული ეფექტურობა | Ელექტროენერგიის გამოტანა · საწვავის ენერგიის შეყვანა × 100 | 30-45% (ISO 3046 სტანდარტები) |
| Საწვავისა და ელექტროენერგიის თანაფარდობა | Კვთ/სთ წარმოებული ელექტროენერგიის მიხედვით გამოყენებული საწვავის გრამები | 180-220 გ/კვთ·სთ (ბუნებრივი აირი) |
Თერმული ეფექტურობა აღწევს მაქსიმუმს 70-85% ტვირთზე, რადგან წვის ტემპერატურები ოპტიმიზირებულია, ხოლო საწვავისა და ელექტროენერგიის თანაფარდობა გაუარესდება 15-30%-ით ხანგრძლივი უმოქმედობის ან ხშირი ჩართვის-გამორთვის ციკლების დროს.
Ტიპიური ბუნებრივი აირის გენერატორების ეფექტურობის მაჩვენებლები სტანდარტულ პირობებში
ISO 3977-2 ტესტირების პროტოკოლების თანახმად (15°C, ზღვის დონე, 60% ფარდობითი ტენიანობა), საკომერციო აირის გენერატორები აჩვენებენ:
- Მარტივი ციკლის ეფექტურობა: 33-38% 500 კვტ-დან 2 მვტ-მდე მოწყობილობებისთვის
- Კომბინირებული თბო- და ელექტროენერგიის (CHP) ეფექტიანობა: 75-85%, როდესაც გამოყენებულია გამოდინების თბო
- Საწვავის მრავალფეროვნების პენალტი: 2-5% ეფექტიანობის დაქვეითება ბიოგაზის გამოყენებისას მილსადენის გაზის შედარებით
2024 წლის DOE-ის ანალიზმა აჩვენა 39,7% საშუალო ეფექტიანობა ახალი ბუნებრივი გაზის გენერატორებისთვის ოპტიმალური нагрузкის პირობებში, რაც 12%-ით მეტია 2015 წლის მოდელებთან შედარებით, კერამიკული გამოდინების რეკუპერატორების და ადაპტური ignition timing-ის წყალობით.
Დიზელი vs. გაზის გენერატორის საწვავის ეფექტიანობა: ენერგიის სიმჭიდროვე და წვის განსხვავებები
Უმეტესი დიზელგენერატორი მუშაობს დაახლოებით 30-დან 35 პროცენტამდე თერმული ეფექტურობით, რადგან ისინი წვავენ საწვავს, რომელსაც ბევრად მეტი ენერგეტიკული სიმჭიდროვე აქვს, ვიდრე ბუნებრივ გაზს. შეხედეთ ციფრებს: დიზელს აქვს დაახლოებით 139,000 BTU/გალონი, მაშინ როდე ბუნებრივ გაზს – მხოლოდ 1,000 BTU/კუბური ფუტი. ამიტომ დიზელის ძრავები თითოეული საწვავის ერთეულიდან მეტ სიმძლავრეს იღებენ, განსაკუთრებით მაშინ, როდესაც მძიმე დატვირთვის პირობებში მუშაობენ. მეორე მხრივ, გაზის გენერატორებს ენერგეტიკული სიმჭიდროვე ნაკლები აქვთ, მაგრამ მაინც აქვთ თავისი უპირატესობები. ისინი უფრო სუფთად წვიან ნაპრალის ignition ტექნოლოგიის წყალობით და ჩვეულებრივ აღწევენ 25-დან 30 პროცენტამდე ეფექტურობას, როდესაც ყველაფერი სწორად მუშაობს გაუთვალისწინებელი რყევების გარეშე.
| Მეტრი | Დიზელის გენერატორი | Გაზის გენერატორი |
|---|---|---|
| Ენერგიის სიმკვრივე | 139,000 BTU/გალონი | 1,000 BTU/კუბური ფუტი (NG) |
| Თერმული ეფექტურობა | 30-35% | 25-30% |
| Იდეალური ტვირთის დიაპაზონი | 70-100% | 50-85% |
Ექსპლუატაციის ხარჯები და გრძელვადიანი ენერგეტიკული დანაზოგი გაზის სიმძლავრის გენერატორულ სისტემებში
Დიზელის აგრეგატებისთვის საწყისი ფასი ნამდვილად უფრო დაბალია, მაგრამ ბუნებრივ აირზე მუშავების გენერატორებზე გადასვლის შემთხვევაში დაწესებულებები აღნიშნავენ დაახლოებით 15-დან 20 პროცენტამდე დანაზოგს საწვავის ხარჯებში ათწლეულის განმავლობაში, როდესაც ისინი ბუნებრივ აირის მილსადენებთან არიან დაკავშირებული. დიზელის საწვავის შემთხვევაში მომსახურების ინტერვალები დაახლოებით 30 პროცენტით უფრო ხშირია, ვიდრე აირის მოდელების შემთხვევაში, თუმცა დიზელის ძრავები საერთო ჯამში 20-დან 30 წლამდე გრძელდება, მაშინ როდესაც აირის ანალოგები მხოლოდ 10-დან 15 წლამდე. იმ სამრეწველო საწარმოებისთვის, რომლებიც მთელი დღის განმავლობაში სტაბილურ ტვირთზე მუშაობენ, აქ ნამდვილი თანხის დანაზოგია შესაძლებელი. ზოგიერთი ოპერაცია აღნიშნავს წლიური ხარჯების შეკვეცას თითქმის თვრამეტი ათასი დოლარით, უბრალოდ იმით, რომ აირის გენერატორები სტრატეგიულად მუშაობს იმ იაფი ღამის საათებში. ეს ლოგიკურია, როდესაც გრძელვადიან ექსპლუატაციის ბიუჯეტებს ვხედავთ.
Აირის გამოყენების გამოყოფილი ნარჩენების პროფილი და რეგულატორული უპირატესობები დიზელის მიმართ
Გაზით მუშავი გენერატორები დაახლოებით 30 პროცენტით ნაკლებ ნახშირორჟანგს და 90 პროცენტით ნაკლებ ნაწილაკებს გამოყოფენ დიზელის ანალოგებთან შედარებით, რაც ნიშნავს, რომ ისინი მკაცრ საერთაშორისო სტანდარტებს უჭირდებიან გარკვეული რთული პირობების გარეშე. იმ ფაქტმა, რომ ეს მოწყობილობები მნიშვნელოვნად ნაკლებ ოქსიდირებულ აზოტს გამოყოფს, ბიზნესი შესაძლებლობა აქვს თავიდან აიცილოს ჯარიმები, რომლებიც დაკავშირებულია ჰაერის ხარისხის ზონებთან, ამიტომ ბევრი კომპანია მათ უპირატესობას ანიჭებს, განსაკუთრებით ქალაქების ან დასახლებული ადგილების ახლოს მუშაობისას. 2023 წლის ზოგიერთი ახალი კვლევის მიხედვით, ბუნებრივ გაზზე გადასვლამ შესაძლოა შეამციროს წლიური ემისია 12-დან 18 ტონამდე იმ კომპანიებისთვის, რომლებიც კომერციული მასშტაბის მოწყობილობებს იყენებენ დიზელის საწვავის გამოყენების ნაცვლად.
Მაქსიმალური გაზის გენერატორის ეფექტიანობისთვის დატვირთვის მართვის ოპტიმიზაცია
Ეფექტური დატვირთვის მართვა პირდაპირ განსაზღვრავს საწვავის მოხმარებას და ოპერაციულ ხარჯებს გაზის ელექტროგენერატორებში. თანამედროვე სისტემები აღწევენ მაქსიმალურ ეფექტურობას მხოლოდ მაშინ, როდესაც ოპერატორები ელექტრო მოთხოვნილებას ზუსტად დაპროექტებულ დატვირთვის დიაპაზონებთან აწონასწორებენ.
Ნახევრად დატვირთვის გავლენა გაზის გენერატორის ეფექტურობაზე
50%-ზე ნაკლები დატვირთვით მუშაობისას თერმული ეფექტურობა 15-30%-ით მცირდება, რადგან წვის камერები ვერ აღწევენ ოპტიმალურ ტემპერატურას. ეს "wet stacking" ეფექტი იწვევს დაუწვავი საწვავის გამოყოფის გაზრდას და ძრავის კომპონენტების დეგრადაციას.
Იდეალური მუშაობის დიაპაზონი (70-85% დატვირთვა) ოპტიმალური საწვავის ეფექტურობისთვის
Აშშ-ის ენერგეტიკის დეპარტამენტის 2022 წლის კვლევამ აჩვენა, რომ 70-85% დატვირთვის დიაპაზონში მოთავსებული გენერატორები 22%-ით მეტ საწვავისგან ელექტროენერგიის გარდაქმნას ახდენენ, ვიდრე 40%-იანი სიმძლავრის მქონე მოწყობილობები. ეს დიაპაზონი მინიმუმამდე ამცირებს მექანიკურ დატვირთვას და უზრუნველყოფს სრულყოფილ საწვავის წვას.
Შემთხვევის ანალიზი: სამრეწველო საწარმო დინამიური დატვირთვის აწონასწორებით საწვავის მოხმარება 18%-ით შეამცირა
Ტეხასში მდებარე საწარმოო საწყობმა შეაერთა ავტომატიზებული დატვირთვის კონტროლერები 2 მეგავატიანი ბუნებრივი გაზის გენერატორების ექვს ერთეულთან, რომლებიც სინქრონიზებულია მანქანების რეალურ დროში მოთხოვნილ დატვირთვასთან. სისტემის პროგნოზირების ალგორითმებმა წლიური საწვავის მოხმარება შეამცირა 18,000 გალონით, ხოლო საშუალო დატვირთვა 78%-ზე დარჩა.
Სტრატეგია: რეალურ დროში მონიტორინგი და ენერგიის მეტრინგის ინტეგრაცია
Თანამედროვე გაზის გენერატორების მოწყობილობები იყენებენ IoT-შესაძლებლობის მქონე სენსორებს, რომლებიც აკონტროლებენ ძაბვის სტაბილურობას (±2%-ის დაშვებით) და გამოდინების ტემპერატურას (600-750°F ოპტიმალური). ღრაბლოვან ენერგეტიკულ დაფებთან ერთად, ეს ინსტრუმენტები საშუალებას აძლევს ოპერატორებს დატვირთვის კორექტირება 30 წამში შეასრულონ.
Მიმდინარეობა: ხელოვნური ინტელექტით მოძრავი დატვირთვის პროგნოზირება გაუმჯობესებს გამოყოფის ეფექტიანობას
Ნეირონული ქსელები, რომლებიც ანალიზებენ ისტორიულ მოთხოვნის მონაცემებს, ახლა საათობრივ დატვირთვის მოთხოვნებს 93% სიზუსტით ანგარიშობს. ეს საშუალებას აძლევს ოპერატორებს წინასწარ გაუშალონ გენერატორები, რითაც ცივი გაშვების ციკლები 41%-ით შემცირდა და წლიური საწვავის ხარჯები 15%-ით დანაკლებული გახდა.
Განვითარებული ტექნოლოგიები გაზის გენერატორების საწვავის ეკონომიას ამაღლებენ
Ეკო-რეჟიმი და ინტელექტუალური ფუნქციები: ავტო-ჩართვა, ცვლადი სიჩქარის გადაცემა
Დღევანდელი გაზის გენერატორები ინტელექტუალური კონტროლის სისტემებით არის აღჭურვილი, რომლებიც მოწყობილობის მოთხოვნიდან მოპყრობის მიხედვით მუშაობის პარამეტრებს მორგებულობენ. ეკო-რეჟიმში მუშაობისას ასეთი მოწყობილობები ცვლად სიჩქარიან გადაცემას უმატებენ პლავნ ჩართვის ფუნქციას, რაც უძრავი მდგომარეობის დროს საწვავის დანახარჯს ამცირებს დაახლოებით 27%-ით უფრო მეტად, ვიდრე ძველი ფიქსირებული სიჩქარის მქონე მოდელები, რაც დამტკიცებულია ინდუსტრიული ტესტების მიერ. მათი განსხვავებული ნიშანი ის არის, რომ ისინი ძრავის შემცირებული სამუშაო სიჩქარის (RPM) დროსაც ძაბვის სტაბილურობას ინარჩუნებენ. ეს განსაკუთრებით ეფექტურია ისეთი ადგილებისთვის, სადაც ელექტროენერგიის მოთხოვნა მუდმივად იცვლება, მაგალითად სავაჭრო ცენტრები ან ახლად გამოჩენილი ჰიბრიდული მიკროქსელები.
Მოწინავე წვის კონტროლის სისტემები და ნაგავის თბოს გამოყენების სისტემები
Მეოთხე თაობის ღურგის წვის ტექნოლოგია, რომელიც ეფუძნება ჰაერ-საწვავის შეფარდების ადაპტურ კონტროლს, აღწევს 94%-იან წვის ეფექტურობას უახლეს ბუნებრივ აირზე მომუშავე გენერატორებში. კომბინირებული სითბოსა და ელექტროენერგიის (CHP) კონფიგურაციები კიდევ უფრო გაზრდის ენერგოეფექტურობას, რადგან გამოყვანილი სითბო გადამისამართებულია:
- Სივრცის გათბობა სითბომიმღებების მეშვეობით
- Აბსორბციული გაცივება გაგრილების სისტემებისთვის
- Სამრეწველო პროცესების გათბობა
Ეს მიდგომა სისტემის სრულ ეფექტურობას 45%-დან 72-78%-მდე ზრდის CHP რეჟიმში.
Შემთხვევის შესწავლა: ინტელექტუალური ინვერტორებით აღჭურვილი მიკროქსელა აუმჯობესებს სისტემის ეფექტურობას
Აშშ-ის შუა ზოლში მდებარე 10 მეგავატიანი სამრეწველო მიკროქსელა მიაღწია წლიური საწვავის 22%-იან ეკონომიას ბუნებრივ აირზე მომუშავე გენერატორების, ქსელის ფორმირების ინვერტორების და აკუმულატორული საწყობის ინტეგრაციით. სისტემა დინამიურად აკოორდინირებს ენერგიის წყაროებს რეალურ დროში ფასებისა და მოთხოვნის სიგნალებზე დაყრდნობით და შენარჩუნებს გენერატორებს მათ 72-78%-იან ირგვლივ ოპტიმალურ ეფექტურობის ზოლში სამუშაო საათების 89%-ში.
Მიდგომა: ჰიბრიდული მზის-აირის კონფიგურაციები პიკური ტვირთის შესამსუბუქებლად და საწვავის შესამცირებლად
Საინდუსტრიო სფეროში მოქმედი ოპერატორები მზის პანელებს მთლიანად ასოცირებენ ტრადიციულ გაზის გენერატორებთან ამ სპეციალური ორმხრივი ინვერტორების საშუალებით, რომლებიც საშუალებას აძლევენ გადართვას ერთი წყაროდან მეორეზე ხელშეუხებლად. მზის მუდმივი განათების პერიოდში, ძირეული ელექტროენერგიის მოთხოვნილებები ძირებში მოწოდდება მზის ენერგიის ხარჯზე, რაც აძლევს გაზის გენერატორებს შესაძლებლობას უბრალოდ იდლინგში იმუშაოს მანამ, სანამ მათი ნამდვილი გამოყენება არ მოხდება. ამ კონფიგურაციამ გაზის აგრეგატების ექსპლუატაციის დრო შეამცირა 40-დან 60 პროცენტამდე იმ რეგიონებში, სადაც მზის განათება წლის განმავლობაში საკმაოდ მდიდარია. ზოგიერთმა საწარმომ თერმული შენახვის სისტემების ჩართვაც დაიწყო, რომლებიც ზედმეტ მზის ენერგიას იყენებს გენერატორებში შემოსული ჰაერის გასათბობად. შედეგად კი? ცივი დაწყებები გაცილებით ეფექტური ხდება, ზოგიერთი საწარმო კი აღნიშნავს დაახლოებით 18%-იან გაუმჯობესებას მოწყობილობების გამოყენების შეწყვეტის შემდეგ მათი გაშვების ეფექტურობაში.
Მომსახურება, საწვავის ხარისხი და ოპერაციული ჩვევები ეფექტიანობაზე გავლენას ახდენენ
Როგორ ზემოქმედებს საწვავის ტიპი შესრულებაზე: მეთანის შემცველობა და მინარევები ბუნებრივ აირში
Აირის ელექტროგენერატორის ეფექტიანობა დამოკიდებულია საწვავის შემადგენლობაზე. მილსადენის ბუნებრივი აირი, რომელიც შეიცავს ≥90% მეთანს, უზრუნველყოფს ოპტიმალურ შესრულებას, ხოლო მინარევები, როგორიცაა გოგირდწყალბადი ან ტენი, შეიძლება შეამციროს ეფექტიანობა 8-12%-ით. მაღალი მეთანის შემცველობის საწვავი უზრუნველყოფს სრულ წვას, ხოლო მინარევები იძულებს ძრავებს მეტი მუშაობის გაკეთებას გამოტანის შესანარჩუნებლად.
Ბიოაირი წინააღმდეგობაში მილსადენის ბუნებრივ აირთან: ეფექტიანობის კომპრომისები და ძრავის ადაპტაცია
Მიუხედავად იმისა, რომ ბიოაირი 60%-ით ამცირებს ნახშირბადის შედეგს მილსადენის აირთან შედარებით, მისი დაბალი ენერგეტიკული სიმჭიდროვე (20-30 მჯ/მ³ წინააღმდეგ 35-40 მჯ/მ³-ის) მოითხოვს მოდიფიცირებული წვის სისტემებს. უმეტეს თანამედროვე აირის გენერატორს ახლა აქვს გასასვენი ნარევის რეგულირებადი მიქსერები, რათა ორივე საწვავის გამოყენება შეუძლიათ ეფექტიანობის დაკარგვის გარეშე.
Შესანარჩუნებელი მომსახურების როლი აირის გენერატორის ეფექტიანობის შენარჩუნებაში
Რეგულარული მომსახურება იცავს აირის ელექტროგენერატორის საწყისი ეფექტიანობის 97-99%-ს მისი სიცოცხლის მთელი ხანის განმავლობაში. მნიშვნელოვანი ამოცანები შედის:
- Ყოველთვიური ჰაერის ფილტრის შეცვლა (თავიდან ავიცილებთ 15%-იან ეფექტურობის დაქვეითებას)
- Წლიური საკრეხის გადაკეთება (შეინარჩუნებს სინქრონიზაციის სიზუსტეს)
- Ყოველმესამე მავთულის სისტემის გამორეცხვა (თავიდან ავიცილებთ 5-8%-იან თერმული ეფექტურობის დაკარგვას)
Კვლევები აჩვენებს, რომ სისტემატური მოვლის პროგრამები წლიურ საწვავის ეკონომიას 10%-ით აუმჯობესებს
Შემთხვევის შესწავლა: ეფექტურობის 14%-იანი მოგება გადაკეთების შემდეგ – უბანის საავადმყოფოს რეზერვული სისტემა
Უბანის საავადმყოფომ შეამცირა 2 მეგავატიანი გაზის გენერატორის საწვავის მოხმარება 0.42-დან 0.36 მ³/კვტ·სთ-მდე შემდეგი ღონისძიებების შედეგად:
- Ტურბო კომპრესორის ლопატების გაწმენდა (2,800 დოლარის ინვესტიცია)
- Გამოშვებული აირების რეცირკულაციის კლაპანის კალიბრაცია
- NOx სენსორის რეალურ დროში ინტეგრაცია
Აღნიშნულმა გაუმჯობესებებმა თავისი ღირებულება 11 თვეში აანაზღაურა შემცირებული შეძენილი სითხის ბუნებრივი გაზის ხარჯების ხარჯებით
Ჩვევები, რომლებიც ეფექტურობას ზიანს აყენებს: უსამართლო გამოყენება, ცივი დაწყება და არასწორი ზომირება
30%-ზე ნაკლები нагрузкиს შემთხვევაში 20 წუთზე მეტი ხნის განმავლობაში ეფექტურობა 22%-ით მცირდება. ხშირად გვხვდება შემდეგი ხარჯობითი პრაქტიკები:
- Ცივი დაწყება წინასწარი სმეხვარის გარეშე : ამატებს ცემინებას 300%-ით
- Ზომის გადაჭარბებული ერთეულები : 150%-ით ზომის გადაჭარბებული გენერატორი ნაწილობრივი нагрузкის დროს 18%-ით მეტ საწვავს ამბოხებს
- Კვირეული სატესტო გაშვებები, რომლებიც 15 წუთს აღემატება : წლიურად 6-9% საწვავის დანახარჯში წვილის წვდომას
Ხელიკრული
Რა უპირატესობა აქვს გაზზე მოძრავ გენერატორებს დიზელის გენერატორების მიმართ?
Გაზზე მოძრავ გენერატორებს ჩვეულებრივ ნაკლები ემისია აქვთ, რაც შეესაბამება მკაცრ გარემოსდაცვით მოთხოვნებს და ამცირებს ნახშირორჟანგისა და ნაწილაკების გამოყოფას დიზელის გენერატორებთან შედარებით.
Როგორ მოქმედებს მოვლა-პატრონობა გაზის გენერატორების ეფექტურობაზე?
Რეგულარული მომსახურება შეძლებს გაზის გენერატორის საწყისი ეფექტიანობის 99%-მდე შენარჩუნებას მისი სიცოცხლის მანძილზე, რაშიც შედის ჰაერის ფილტრების შეცვლა, საცენი შთამავლების შეკეთება და სითბოგამტარობის სისტემის გარეცხვა.
Შეიძლება თუ არა გაზის გენერატორებმა ეფექტურად გამოიყენონ როგორც მილსადენის ბუნებრივი გაზი, ასევე ბიოგაზი?
Დიახ, თანამედროვე გაზის გენერატორები ადაპტირებულია ორივე საწვავის ეფექტურად გამოსაყენებლად რეგულირებადი ჰაერ-საწვავის მიქსერებით, თუმცა ბიოგაზს აქვს დაბალი ენერგეტიკული სიმკვრივე, რაც მოითხოვს განსხვავებულ წვის სისტემებს.
Რატომ ასრულებენ უკეთესად ბუნებრივი გაზის გენერატორების ახალი მოდელები?
Ახალი მოდელები იყენებენ საშუალებებს, როგორიცაა ღია წვის ტექნოლოგია და გაუმჯობესებული გაგრილების მექანიზმები, რაც უზრუნველყოფს უკეთეს ეფექტიანობას და სითბოს დაკარგვის შემცირებას.
Შინაარსის ცხრილი
- Რა არის ენერგეტიკული ეფექტიანობა გენერატორულ აგრეგატებში?
- Ეფექტურობის გაზომვა: თერმული ეფექტურობა და საწვავიდან ელექტროენერგიის გარდაქმნა
- Ტიპიური ბუნებრივი აირის გენერატორების ეფექტურობის მაჩვენებლები სტანდარტულ პირობებში
- Დიზელი vs. გაზის გენერატორის საწვავის ეფექტიანობა: ენერგიის სიმჭიდროვე და წვის განსხვავებები
- Ექსპლუატაციის ხარჯები და გრძელვადიანი ენერგეტიკული დანაზოგი გაზის სიმძლავრის გენერატორულ სისტემებში
- Აირის გამოყენების გამოყოფილი ნარჩენების პროფილი და რეგულატორული უპირატესობები დიზელის მიმართ
-
Მაქსიმალური გაზის გენერატორის ეფექტიანობისთვის დატვირთვის მართვის ოპტიმიზაცია
- Ნახევრად დატვირთვის გავლენა გაზის გენერატორის ეფექტურობაზე
- Იდეალური მუშაობის დიაპაზონი (70-85% დატვირთვა) ოპტიმალური საწვავის ეფექტურობისთვის
- Შემთხვევის ანალიზი: სამრეწველო საწარმო დინამიური დატვირთვის აწონასწორებით საწვავის მოხმარება 18%-ით შეამცირა
- Სტრატეგია: რეალურ დროში მონიტორინგი და ენერგიის მეტრინგის ინტეგრაცია
- Მიმდინარეობა: ხელოვნური ინტელექტით მოძრავი დატვირთვის პროგნოზირება გაუმჯობესებს გამოყოფის ეფექტიანობას
-
Განვითარებული ტექნოლოგიები გაზის გენერატორების საწვავის ეკონომიას ამაღლებენ
- Ეკო-რეჟიმი და ინტელექტუალური ფუნქციები: ავტო-ჩართვა, ცვლადი სიჩქარის გადაცემა
- Მოწინავე წვის კონტროლის სისტემები და ნაგავის თბოს გამოყენების სისტემები
- Შემთხვევის შესწავლა: ინტელექტუალური ინვერტორებით აღჭურვილი მიკროქსელა აუმჯობესებს სისტემის ეფექტურობას
- Მიდგომა: ჰიბრიდული მზის-აირის კონფიგურაციები პიკური ტვირთის შესამსუბუქებლად და საწვავის შესამცირებლად
-
Მომსახურება, საწვავის ხარისხი და ოპერაციული ჩვევები ეფექტიანობაზე გავლენას ახდენენ
- Როგორ ზემოქმედებს საწვავის ტიპი შესრულებაზე: მეთანის შემცველობა და მინარევები ბუნებრივ აირში
- Ბიოაირი წინააღმდეგობაში მილსადენის ბუნებრივ აირთან: ეფექტიანობის კომპრომისები და ძრავის ადაპტაცია
- Შესანარჩუნებელი მომსახურების როლი აირის გენერატორის ეფექტიანობის შენარჩუნებაში
- Შემთხვევის შესწავლა: ეფექტურობის 14%-იანი მოგება გადაკეთების შემდეგ – უბანის საავადმყოფოს რეზერვული სისტემა
- Ჩვევები, რომლებიც ეფექტურობას ზიანს აყენებს: უსამართლო გამოყენება, ცივი დაწყება და არასწორი ზომირება
-
Ხელიკრული
- Რა უპირატესობა აქვს გაზზე მოძრავ გენერატორებს დიზელის გენერატორების მიმართ?
- Როგორ მოქმედებს მოვლა-პატრონობა გაზის გენერატორების ეფექტურობაზე?
- Შეიძლება თუ არა გაზის გენერატორებმა ეფექტურად გამოიყენონ როგორც მილსადენის ბუნებრივი გაზი, ასევე ბიოგაზი?
- Რატომ ასრულებენ უკეთესად ბუნებრივი გაზის გენერატორების ახალი მოდელები?