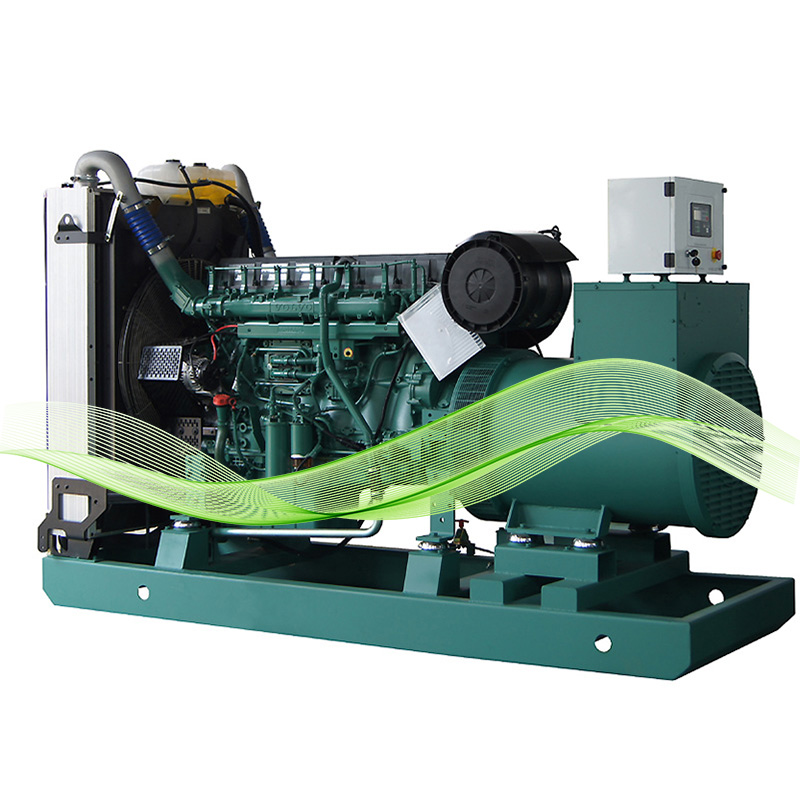
ປະໂຫຍດດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີ້ແກັສ
ໂປຣໄຟລ໌ການປ່ອຍອາຍພິດຕ່ຳຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີ້ແກັດທຳມະຊາດ
ຕາມການຄົ້ນຄວ້າທີ່ຖືກປະກາດໂດຍສະຖາບັນ Ponemon ໃນປີ 2023, ກ່ອນໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັສທຳມະຊາດຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຜ່ອນສານມົນລະພິດໃນຮູບແບບຂອງອົງຄະທີ່ເປັນອັນຕະລາຍລົງປະມານ 45 ເປີເຊັນ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປ່ອຍອາຍໄນໂຕຣເຈນໄອໂອໄຄດ້ວຍປະມານ 30 ເປີເຊັນ ເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບກຸ່ມທີ່ໃຊ້ນ້ຳມັນດີເຊວ. ສິ່ງທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ລະບົບເຫຼົ່ານີ້ເດັ່ນກວ່າຄື ມັນບໍ່ຜະລິດຂີ້ເທົ່າເລີຍ, ເຊິ່ງເປັນສິ່ງສຳຄັນຫຼາຍເວລາດຳເນີນງານໃນເມືອງ ຫຼື ພາຍໃນອາຄານ ທີ່ຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດມີຄວາມໝາຍຫຼາຍທີ່ສຸດ. ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີການຈີກຕົວລ້າສຸດນີ້ໄດ້ຂະຫຍາຍໃຫ້ເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສທີ່ທັນສະໄໝສາມາດບັນລຸລະດັບ NOx ຕ່ຳກວ່າ 0.4 ກຼາມຕໍ່ກິໂລແວັດຊ໌ຕໍ່ຊົ່ວໂມງ. ນີ້ໝາຍຄວາມວ່າ ພວກມັນສາມາດປະຕິບັດຕາມຂໍ້ກຳນົດ Tier 4 ທີ່ເຂັ້ມງວດໂດຍບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງໃຊ້ອຸປະກອນເພີ່ມເຕີມໃນການດຳເນີນງານຫຼັງການປ່ອຍອາຍ, ເຊິ່ງເປັນສິ່ງທີ່ຜູ້ດຳເນີນງານຫຼາຍຄົນຊົມເຊີຍ ທັງເພື່ອຄວາມສອດຄ່ອງ ແລະ ດ້ານຕົ້ນທຶນ.
ການວິເຄາະປຽບທຽບຜົນຜະລິດ CO-, NOx ແລະ ສານມົນລະພິດໃນຮູບແບບຂອງອົງຄະ
ກ່ອນໄຟຟ້າແກັສສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນເຖິງຄວາມເດັ່ນໜ້າດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມໃນທຸກໆສານມົນລະພິດຫຼັກ:
| ປະເພດອາຍພິດ | ເຄື່ອງກໍາເນີດອາຍແກັສ | ເຄື່ອງຜະລິດໄຟຟ້າ diesel | ການຫຼຸດລົງ |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO- (g/kWh) | 450 | 650 | 30.7% |
| NOx (g/kWh) | 0.35 | 2.8 | 87.5% |
| PM (mg/m³) | 9.2 | 84 | 89% |
ຂໍ້ມູນຈາກບົດລາຍງານປີ 2023 ຂອງຫ້ອງທົດລອງພະລັງງານທີ່ຊົດເຊີຍໄດ້ແຫ່ງຊາດ (NREL) ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າລະບົບກັດອາຍແກັສຫຼຸດຜ່ອນສາເຫດຂອງໂອໂຊນລະດັບດິນ 76% ຶ່ງກັບທາງເລືອກດ້ວຍດີເຊວ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດດີຂຶ້ນໃນເຂດທີ່ມີຄົນຢູ່ຫຼາຍ.
ການປະຕິບັດຕາມລະບຽບຂໍ້ກຳນົດ ແລະ ມາດຕະຖານຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດ
ເມືອງໃຫຍ່ສ່ວນຫຼາຍໃນອາເມລິກາມີກົດລະບຽບດ້ານຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດທີ່ເຂັ້ມງວດຫຼາຍ ເຊິ່ງເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟດີເຊວບໍ່ສາມາດໃຊ້ໄດ້ອີກຕໍ່ໄປ ທີ່ຈະຕ້ອງໃຊ້ເງິນຈຳນວນຫຼວງຫຼາຍໃນການປັບປຸງພິເສດ. ໃນດ້ານກົງກັນຂ້າມ, ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັດສາມາດເຂົ້າກັນໄດ້ຕາມຂໍ້ກຳນົດຂອງກົດໝາຍວ່າດ້ວຍອາກາດສະອາດຂອງ EPA ແລະ ມາດຕະຖານຂັ້ນເຂັ້ມງວດຂອງລັດຄາລິຟໍເນຍ (CARB) ທີ່ກຳນົດໄວ້ສຳລັບປີ 2024. ຕາມການຄົ້ນຄວ້າອຸດສາຫະກໍາໃນປີຜ່ານມາ, ບັນດາທຸລະກິດທີ່ກໍາລັງພິຈາລະນາການປ່ຽນມາໃຊ້ແກັດຈະພົບວ່າຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງປັບປຸງໜ້ອຍລົງປະມານ 92 ເປີເຊັນ ເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບການໃຊ້ດີເຊວໃນເຂດທີ່ຖືກຄວບຄຸມ. ນີ້ເຂົ້າໃຈໄດ້ງ່າຍ ເນື່ອງຈາກການຈັດການກັບການປັບປຸງເພີ່ມເຕີມເຫຼົ່ານີ້ອາດຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນຢ່າງໄວວາ.
ຄວາມຍືນຍົງດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມໃນໄລຍະຍາວຂອງການໃຊ້ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟແກັດ
ຕາມການຄົ້ນຄວ້າບາງຢ່າງທີ່ອອກມາຈາກຫ້ອງທົດລອງແຫ່ງຊາດອາໂກນເນ (Argonne National Lab) ໃນປີ 2022 ກ່າວວ່າ, ກ່ອງເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ກັດສະດີທຳມະຊາດທີ່ຖ້າມາ (RNG) ເປັນເຊື້ອໄຟນັ້ນ ຕົວຈິງແລ້ວກາຍເປັນຜູ້ປ່ອຍກາກບອນໃນຮູບແບບລົບ. ລຸ້ນໃໝ່ຍັງມີຄວາມສາມາດທີ່ໜ້າປະທັບໃຈອີກດ້ວຍ, ໂດຍການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການລົ້ນຂອງມີເທນ (methane slip) ໄດ້ເຖິງປະມານ 0.2% ຂອງປະລິມານທີ່ເຂົ້າໄປ ເນື່ອງຈາກການປິດຊິດທີ່ດີຂຶ້ນ ແລະ ການອອກແບບທີ່ແໜ້ນໜາຂຶ້ນ. ການພິຈາລະນາຕະຫຼອດວົງຈອງຊີວິດຂອງມັນ ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ເຄື່ອງຈັກທີ່ໃຊ້ກັດສະດີເຫຼົ່ານີ້ ສ້າງອາຍິເຮືອນແກ້ວໜ້ອຍກວ່າເຄື່ອງຈັກດີເຊວໄດ້ປະມານ 58% ໃນໄລຍະ 15 ປີ. ຂໍ້ມູນນີ້ຖືກກວດກາປຽບທຽບກັບກົດເກນດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມມາດຕະຖານ ISO 14040 ຈາກປີ 2021, ດັ່ງນັ້ນພວກເຮົາຈຶ່ງຮູ້ວ່າ ມັນບໍ່ແມ່ນພຽງແຕ່ການໂຄສະນາເທົ່ານັ້ນ.
ປະສິດທິພາບດ້ານຕົ້ນທຶນການດຳເນີນງານ ແລະ ຄວາມງ່າຍດາຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ
ຕົ້ນທຶນເຊື້ອໄຟ ແລະ ຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງຂອງລາຄາ ສຳລັບເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ກັດສະດີ ເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບດີເຊວ
ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ກັດສະດີສາມາດສະໜອງ 20–25% ຕົ້ນທຶນເຊື້ອໄຟປະຈຳປີທີ່ຕ່ຳກວ່າ ເມື່ອທຽບກັບຮຸ່ນດີເຊວ, ມີການສະໜັບສະໜູນຈາກລາຄາແກັສທຳມະຊາດທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຕ່ຳກວ່າລາຄາດີເຊວປະມານ 30% (EIA 2023). ແກັສທີ່ສະໜອງຜ່ານທໍ່ໄດ້ຫຼີກເວັ້ນຄວາມຜັນຜວນຂອງລາຄາທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບເຫດການດ້ານພູມສາດການເມືອງ ຫຼື ການຂາດຕອນໃນຫ້ອງການສະໜອງ ທີ່ບໍ່ຄືກັບດີເຊວ ເຊິ່ງຂຶ້ນກັບຜົນຜະລິດຈາກໂຮງກົງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ.
| ປັດໃຈດ້ານຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ | ເຄື່ອງປ້ອມລະຫວ່າງຂຳໆ | เครื่องกำเนิดไฟฟ้าดีเซล |
|---|---|---|
| ລາຄາເຊື້ອໄຟສະເລ່ຍ (2023) | $3.12/MMBtu | $4.20/ແກວລັນ |
| ຄວາມຜັນຜວນຂອງລາຄາ (5 ປີ) | ±12% | ±38% |
ຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງນີ້ຊ່ວຍໃຫ້ຜູ້ໃຊ້ງານເພື່ອການຄ້າສາມາດຄາດເດົາຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍດ້ານການດຳເນີນງານໃນໄລຍະຍາວໄດ້ຢ່າງຖືກຕ້ອງ.
ການປຽບທຽບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍດ້ານການດຳເນີນງານລະຫວ່າງເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສ ແລະ ດີເຊວ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍດ້ານການບຳລຸງຮັກສາສຳລັບເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສ ຕ່ຳກວ່າ 15–20% , ເນື່ອງຈາກການປ່ຽນຕົວກອງນ້ຳມັນເຊື້ອໄຟທີ່ໜ້ອຍລົງ ແລະ ບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງໃຊ້ລະບົບຂອງແຫຼວພິດ (DEF). ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນໄລຍະຊີວິດ (lifecycle cost) ປີ 2023 ຂອງອຸປະກອນ 500 kW ໄດ້ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ, ກ່ອນກຳເນີດແຮງໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັສ ສາມາດປະຢັດຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃຫ້ຜູ້ດຳເນີນງານໄດ້ $18,000–$22,000 ຕໍ່ປີ ໃນດ້ານຄ່ານ້ຳມັນ ແລະ ການບຳລຸງຮັກສາລວມກັນ ຖ້າທຽບກັບແບບທີ່ໃຊ້ດີເຊວ.
ຄວາມສັບສົນໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ ແລະ ຄວາມງ່າຍດາຍໃນການດຳເນີນງານຂອງລະບົບແກັສ
ການຈັບຕົວທີ່ສະອາດຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການສະສະสมຂອງກາກບອນ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ໄລຍະເວລາການບຳລຸງຮັກສາເຄື່ອງຈັກຍາວຂຶ້ນ 30–40%. ໂດຍບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງເຮັດຄວາມສະອາດຫัวສີດເຊື້ອໄຟເລື້ອຍໆ ຫຼື ລະບົບຄວບຄຸມການປ່ອຍອາຍພິດທີ່ສັບສົນ, ກ່ອນກຳເນີດແຮງໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັສຈຶ່ງໃຊ້ອົງປະກອບມາດຕະຖານທີ່ເຂົ້າກັນໄດ້ກັບໂຄງລ່າງພື້ນຖານ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ເວລາລົງໄປບຳລຸງຮັກສາຫຼຸດລົງ 25%.
ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືຂອງການສະໜອງເຊື້ອໄຟ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມໂລ້ງກັບໂຄງລ່າງພື້ນຖານ
ການສະໜອງເຊື້ອໄຟຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງຜ່ານການເຊື່ອມໂລ້ງກັບເຄືອຂ່າຍໄຟຟ້າ
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັສເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ໂດຍກົງກັບທໍ່ແກັສທໍາມະຊາດຂອງເມືອງ, ຮັບປະກັນການເຂົ້າເຖິງເຊື້ອໄຟຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງໂດຍບໍ່ຈໍາເປັນຕ້ອງເຕີມນ້ຳມັນດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ. ຕາມລາຍງານດ້ານຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງດ້ານພະລັງງານ DOE 2023, 93% ຂອງເຂດພານິຊຍະກຳໃນເມືອງຮັກສາທໍ່ສົ່ງແກັສທີ່ມີຄວາມດັນໄດ້ໃນຊ່ວງທີ່ໄຟຟ້າດັບ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ສາມາດດຳເນີນງານຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງເວລາທີ່ໄຟຟ້າຂາຍດັບ.
ການມີຢູ່ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດໃນການເຂົ້າເຖິງເຊື້ອໄຟໃນຊ່ວງເວລາເກີດເຫດສຸກເສີນ
ທໍ່ສົ່ງແກັສທີ່ຝັງຢູ່ໃຕ້ດິນມີອັດຕາການລົບກວນການບໍລິການໜ້ອຍກວ່າ 78% ສົມທຽບກັບເສັ້ນທາງການຈັດສົ່ງນ້ຳມັນດີເຊວທີ່ຢູ່ເທິງດິນໃນຊ່ວງອາກາດເລີ່ມຮ້າຍແຮງ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ມີຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງຫຼາຍຂຶ້ນໃນຊ່ວງເວລາເກີດໄພພິບັດ. ຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງນີ້ມີຄວາມສຳຄັນຕໍ່ໂຮງໝໍ, ສູນຂໍ້ມູນ, ແລະ ສະຖານທີ່ສຳລັບການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອເຫດສຸກເສີນທີ່ຕ້ອງການການດຳເນີນງານຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງ 99.99%.
ຂໍ້ກຳນົດການເກັບຮັກສາເຊື້ອໄຟ ແລະ ຂໍ້ພິຈາລະນາດ້ານຄວາມປອດໄພ
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັສບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງມີການເກັບຮັກສາເຊື້ອໄຟຢູ່ສະຖານທີ່, ຕ່າງຈາກລະບົບດີເຊວທີ່ຕ້ອງການຖັງເກັບ 500–1,000 ແກລອນຂຶ້ນໄປ ແລະ ການປ່ຽນຖ່າຍນ້ຳມັນທຸກອາທິດ:
| ປັດຈຳ | ເຄື່ອງກໍາເນີດອາຍແກັສ | ເຄື່ອງຜະລິດໄຟຟ້າ diesel |
|---|---|---|
| ການເກັບຮັກສາເຊື້ອໄຟຢູ່ສະຖານທີ່ | 0 ແກລອນ | 500-1,000+ ແກລອນ |
| ຄວາມສ່ຽງໄຟໄໝ້ (NFPA 110) | ຊັ້ນ 1 | ຊັ້ນ 3 |
| ຊ່ວງເວລາການແມ່ນຕໍ | 150–200 ຊົ່ວໂມງ | 50–100 ຊົ່ວໂມງ |
ການລຶບລ້າງການຈັດເກັບສິນຄ້າໃນຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່ ຈະຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງໄຟໄໝ້ລົງ 83% (ຂໍ້ມູນຈາກ NFPA) ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍປີະຈໍາປີໃນການຈັດການເຊື້ອໄຟລົງ $7,500–$15,000 ສຳລັບເວັບໄຊທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການຄ້າ.
ປະສິດທິພາບດ້ານສຽງແລະຄວາມເໝາະສົມໃນເຂດຕົວເມືອງຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີໄຟຟ້າແຮງດັນສູງ
ລະດັບສຽງແລະກິ່ນຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແຮງດັນສູງໃນເຂດຕົວເມືອງ
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແຮງດັນສູງເຮັດວຽກຢູ່ລະດັບ 60–80 ເດຊິເບວ – ເທົ່າກັບສຽງພື້ນຖານໃນຮ້ານອາຫານ – ແລະ ມີສຽງດັງໜ້ອຍກວ່າ 15–30% ຂອງເຄື່ອງດີເຊວ, ເຊິ່ງປົກກະຕິຈະປ່ອຍສຽງ 75–100+ ເດຊິເບວ. ການຈັດເຜົາທີ່ສະອາດກວ່ານີ້ຈະຜະລິດກິ່ນຈາກທໍ້ລະບາຍໜ້ອຍທີ່ສຸດ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ມັນເໝາະສົມສຳລັບໂຮງໝໍ, ໂຮງຮຽນ ແລະ ການພັດທະນາທີ່ປະສົມປະສານກັນ ເຊິ່ງຄຸນນະພາບອາກາດ ແລະ ສຽງມີຄວາມໝາຍ.
ເຕັກໂນໂລຊີການດູດຊຶມສຽງໃນເຄື່ອງແຮງດັນສູງທີ່ທັນສະໄໝ
ການອອກແບບຂັ້ນສູງປະກອບມີ ເຄື່ອງຈັກທີ່ມີສຽງລົບກວນຕ່ຳ, ກ້ອງກັ້ນສຽງຫຼາຍຊັ້ນ, ລະບົບໄອເດີທີ່ຖືກອອກແບບມາເພື່ອຫຼຸດສຽງ, ຈຸດຕິດຕັ້ງທີ່ຊ່ວຍດູດຊຶມການສັ່ນສະເທືອນ, ແລະ ການປັບຮູບແບບ RPM ລ່ວງໜ້າ. ດັ່ງທີ່ໄດ້ລະບຸໄວ້ໃນລາຍງານຂອງອຸດສາຫະກໍາປີ 2025 ກ່ຽວກັບການປັບປຸງເຄື່ອງກໍເອນໄຟຟ້າ, ລັກສະນະເຫຼົ່ານີ້ຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຜ່ອນສຽງລົບກວນລົງ 40–60%, ໃນຂະນະທີ່ຮັກສາລະດັບສຽງຕ່ຳກວ່າ 70 ດີບີ ເຖິງແມ່ນໃນສະພາບການໃຊ້ງານສູງສຸດ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ສາມາດຕິດຕັ້ງໃນສະຖານທີ່ເມືອງທີ່ມີຄວາມອ່ອນໄຫວຕໍ່ສຽງລົບກວນ.
ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖື, ເວລາຕອບສະໜອງ ແລະ ຄວາມຍືດຢຸ່ນໃນການນຳໃຊ້
ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືຂອງເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັສທຳມະຊາດໃນຊ່ວງເວລາຂາດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ດົນ
ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບທໍ່ສົ່ງໄຟຟ້າ, ເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັດສາມາດໃຊ້ງານໄດ້ຕະຫຼອດເວລາໃນຊ່ວງຂາດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ດົນ. ລາຍງານດ້ານຄວາມອົດທົນດ້ານພະລັງງານປີ 2023 ພົບວ່າ ພວກມັນສາມາດບັນລຸໄດ້ 98% ຂອງເວລາໃຊ້ງານຕະຫຼອດໄລຍະເວລາຂາດໄຟຟ້າຫຼາຍມື້, ເຊິ່ງສູງກວ່ານ້ຳມັນດີເຊວ 84%. ອັດຕາຂັດຂ້ອງຫຼຸດລົງ 42% ໃນໂຄງລ່າງພື້ນຖານທີ່ສຳຄັນ, ເຊິ່ງສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນເຖິງຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືຂອງພວກມັນ.
ເວລາຕອບສະໜອງໃນການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດໃນການຮັບນ້ຳໜັກ
ເຄື່ອງກໍາເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສທີ່ທັນສະໄໝ ສາມາດບັນລຸຂອບເຂດຄວາມສາມາດເຕັມທີ່ພາຍໃນ 15–30 ວິນາທີ ຫຼັງຈາກການກວດພົບການຂາດໄຟຟ້າ – ໄວຂຶ້ນ 20% ກ່ວາຮຸ່ນດີເຊນທີ່ມີຂະໜາດດຽວກັນ. ການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນຢ່າງວ່ອງໄວນີ້ ຮັບປະກັນການສະຫນັບສະຫນູນຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງສຳລັບອຸປະກອນທີ່ອ່ອນໄຫວ ເຊັ່ນ: ອຸປະກອນການແພດ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງແມ່ຂ່າຍຂໍ້ມູນ. ພວກມັນຍັງສາມາດຮັບໄຟຟ້າໜັກ 100% ໄດ້ທັນທີ, ບໍ່ຕ້ອງມີການເພີ່ມຂຶ້ນຢ່າງຄ່ອຍເປັນຄ່ອຍໄປ ເຊັ່ນດຽວກັບຫຼາຍຮຸ່ນດີເຊນ.
ການເສື່ອມສະພາບການປະຕິບັດງານໃນສະພາບອາກາດຮຸນແຮງ
ເຄື່ອງກໍາເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສຮັກສາການປະຕິບັດງານທີ່ເຊື່ອຖືໄດ້ໃນສະພາບອາກາດຮຸນແຮງ, ໂດຍສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນການສູນເສຍປະສິດທິພາບໜ້ອຍທີ່ສຸດ ເຖິງ -40°F (-40°C) – ເຊິ່ງຫຼີກເວັ້ນບັນຫາເຊື້ອໄຟດີເຊນແຂງຕົວທີ່ເກີດຂຶ້ນບໍ່ຍາກ. ໃນອຸນຫະພູມທີ່ເກີນ 104°F (40°C), ເຄື່ອງແກັສສາມາດຮັກສາຂອບເຂດຜົນຜະລິດໄດ້ 95%, ດີກວ່າດີເຊນ 18 ຈຸດເປີເຊັນໃນໄລຍະທີ່ມີຄວາມຮ້ອນສູງ.
ກໍລະນີການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ເໝາະສົມສຳລັບເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສໃນເຮືອນ ແລະ ທຸລະກິດ
- ບ້ານພັກ : ການສະຫນັບສະຫນູນທັງໝົດໂດຍບໍ່ຈຳກັດການເກັບຮັກສາເຊື້ອໄຟ
- ການຮັກສາສຸຂະພາບ : ການສະຫນອງພະລັງງານຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງສຳລັບລະບົບຊີວິດ
- ການຜະລິດ : ເຄື່ອງຈັກທີ່ຕ້ອງການພະລັງງານສູງ ແລະ ຕ້ອງການການກູ້ຄືນທັນທີ
- ໂທລະຄົມ : ການດຳເນີນງານຫໍຄວບຄຸມໄລຍະໄກດ້ວຍການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ເຂົ້າສູ່ເຄືອຂ່າຍໂດຍອັດຕະໂນມັດ
ຄວາມສາມາດໃນການຂະຫຍາຍຂະຫນາດ ແລະ ການຜະສົມຜະສານກັບລະບົບພະລັງງານທີ່ຍືນຍົງ
ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າແກັສຖືກຜະສົມຢ່າງລຽບລຽງກັບພະລັງງານແສງຕາເວັນ ແລະ ພະລັງງານລົມຜ່ານຕົວຄວບຄຸມຮູບແບບຮິບຣິດ, ເຊິ່ງຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຄວາມຕ້ອງການຂະຫນາດລະບົບພະລັງງານທີ່ຍືນຍົງລົງ 30–40% (ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າດ້ານຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງຂອງເຄືອຂ່າຍປີ 2024). ໃນລະບົບໄຟຟ້າຈຸດ, ມັນເຮັດໜ້າທີ່ເປັນແຫຼ່ງພະລັງງານຖາວອນໃນຊ່ວງເວລາທີ່ພະລັງງານທີ່ຍືນຍົງມີການຜະລິດຕ່ຳ ໃນຂະນະທີ່ຮັກສາລະດັບການປ່ອຍອາຍພິດໃຫ້ຕ່ຳກວ່າເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟດີເຊວ 60%
ຄຳຖາມທີ່ຖາມບໍ່ຍາກ
ຂໍ້ດີດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມຫຼັກໆຂອງເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າແກັສເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟດີເຊວມີຫຍັງແດ່?
ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າແກັສມີຂໍ້ດີດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍ ເຊັ່ນ: ການປ່ອຍອາຍພິດໄນໂຕຣເຈນ, ອາຍຝຸ່ນ ແລະ ອາຍກາກບອນມອນອກໄຊດ້ວຍປະລິມານຕ່ຳ. ພວກມັນຍັງສອດຄ່ອງກັບມາດຕະຖານ EPA ແລະ CARB ທີ່ເຂັ້ມງວດ ແລະ ສາມາດເຮັດໃຫ້ການປ່ອຍອາຍກາກບອນເປັນລົບໄດ້ຖ້າໃຊ້ພະລັງງານທຳມະຊາດທີ່ຍືນຍົງ.
ຕົ້ນທຶນການດຳເນີນງານຂອງເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟຟ້າແກັສ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງປັ່ນໄຟດີເຊວປຽບທຽບກັນແນວໃດ?
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັສປົກກະຕິມີຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍດ້ານເຊື້ອໄຟປະຈໍາປີຕ່ຳກວ່າ 20-25% ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບໍລິການຮັກສາຕ່ຳກວ່າ 15-20% ສົມທຽບກັບເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີດີເຊວ. ພວກມັນຍັງມີຄວາມໝັ້ນຄົງດ້ານລາຄາຫຼາຍຂຶ້ນ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມຕ້ອງການໃນການຈັດການເຊື້ອໄຟ ເນື່ອງຈາກການຂຶ້ນກັບທໍ່ແກັສຂອງເມືອງ.
ຫຍັງເຮັດໃຫ້ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັສເໝາະສົມກັບການນຳໃຊ້ໃນເຂດເມືອງ?
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັສມີສຽງດັງ ແລະ ກິ່ນໜ້ອຍກວ່າເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີດີເຊວ, ເຮັດໃຫ້ພວກມັນເໝາະສົມກັບສະຖານທີ່ເມືອງທີ່ອ່ອນໄຫວຕໍ່ສຽງດັງ. ພວກມັນຍັງບໍ່ຕ້ອງການສະຖານທີ່ເກັບຮັກສາເຊື້ອໄຟໃນສະຖານທີ່, ເຊິ່ງຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງດ້ານໄຟໄໝ້ຢ່າງຫຼວງຫຼາຍ.
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັດມີຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືໄດ້ຫຼາຍປານໃດໃນຊ່ວງເວລາທີ່ໄຟດັບ?
ເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີແກັດມີຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືໄດ້ສູງໃນຊ່ວງເວລາທີ່ໄຟດັບ ເນື່ອງຈາກພວກມັນເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບທໍ່ແກັດຂອງເມືອງ. ພວກມັນສາມາດໃຫ້ໄຟໄດ້ຕະຫຼອດເວລາເຖິງ 98% ໃນຊ່ວງໄລຍະເວລາໄຟດັບທີ່ດົນ, ໂດຍບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງເຕີມເຊື້ອໄຟດ້ວຍຕົນເອງ.
ສາລະບານ
- ປະໂຫຍດດ້ານສິ່ງແວດລ້ອມຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີ້ແກັສ
- ປະສິດທິພາບດ້ານຕົ້ນທຶນການດຳເນີນງານ ແລະ ຄວາມງ່າຍດາຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາ
- ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືຂອງການສະໜອງເຊື້ອໄຟ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມໂລ້ງກັບໂຄງລ່າງພື້ນຖານ
- ປະສິດທິພາບດ້ານສຽງແລະຄວາມເໝາະສົມໃນເຂດຕົວເມືອງຂອງເຄື່ອງກໍເນເຕີໄຟຟ້າແຮງດັນສູງ
-
ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖື, ເວລາຕອບສະໜອງ ແລະ ຄວາມຍືດຢຸ່ນໃນການນຳໃຊ້
- ຄວາມໜ້າເຊື່ອຖືຂອງເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ໃຊ້ແກັສທຳມະຊາດໃນຊ່ວງເວລາຂາດໄຟຟ້າທີ່ດົນ
- ເວລາຕອບສະໜອງໃນການເລີ່ມຕົ້ນ ແລະ ຄວາມສາມາດໃນການຮັບນ້ຳໜັກ
- ການເສື່ອມສະພາບການປະຕິບັດງານໃນສະພາບອາກາດຮຸນແຮງ
- ກໍລະນີການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ເໝາະສົມສຳລັບເຄື່ອງກຳເນີດໄຟຟ້າແກັສໃນເຮືອນ ແລະ ທຸລະກິດ
- ຄວາມສາມາດໃນການຂະຫຍາຍຂະຫນາດ ແລະ ການຜະສົມຜະສານກັບລະບົບພະລັງງານທີ່ຍືນຍົງ
- ຄຳຖາມທີ່ຖາມບໍ່ຍາກ