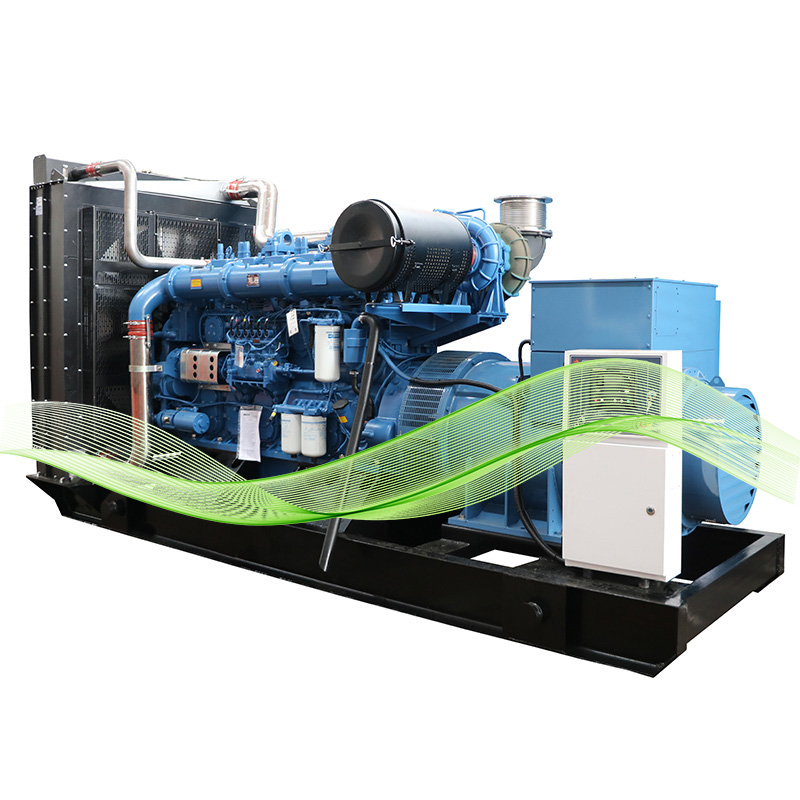
Розуміння основних принципів тихої роботи дизельного генератора
Основний механізм тихої роботи дизельного генератора
Сучасні тихі дизельні генератори пройшли довгий шлях від своїх шумних попередників завдяки вдалому поєднанню акустичного проектування та технологій гасіння вібрацій. Звичайні генератори зазвичай працюють на рівні 75–90 децибел, що є досить голосним для більшості умов. Новіші тихі версії вирішують цю проблему за допомогою кількох підходів одночасно. Вони використовують знайомі нам багатоступеневі глушники, а також спеціальні звукоізоляційні корпуси, які огортають весь агрегат. Деякі навіть мають інтелектуальні системи керування двигуном, які регулюють продуктивність залежно від навантаження. Згідно з дослідженням, опублікованим минулого року, ці інновації фактично зменшують рівень шумового забруднення приблизно на 40 відсотків порівняно зі стандартними моделями. Це робить їх набагато кращим варіантом для місць, де важлива тиха робота.
- Оптимізація згоряння : прецизійне паливне впорскування мінімізує шум детонації
- Утримання : композитні корпуси з вставним згасанням шуму 20–30 дБ блокують повітряні шуми
- Видалення вibracнь : Антивібраційні кріплення відокремлюють механічні вібрації від рами
Основні джерела шуму: механічні, згоряння, вихлоп та вібрація
Чотири переважаючі компоненти шуму потребують цільових заходів зі зменшення:
| Джерело шуму | Частотний діапазон | Типовий внесок |
|---|---|---|
| Механічне тертя | 500–4 000 Гц | 32% від загального обсягу |
| Вихлопні імпульси | 100–1 000 Гц | 28% |
| Динаміка згоряння | 2–5 кГц | 25% |
| Конструкційна вібрація | 20–200 Гц | 15% |
Сучасні конструкції, такі як ті, що описані в сучасних схемах генераторів, посилаються на приглушення високочастотного вихлопу насамперед, оскільки ці тони поширюються найдалі в міських умовах.
Інженерні методи придушення шуму
Виробники застосовують сім перевірених стратегій зниження рівня шуму:
- Системи ізоляції : Компоненти двигуна, обгорнуті бар'єрами з вінілу підвищеної маси (MLV)
- Резонатори Гельмгольца : Налаштовані порожнини компенсують частоти вихлопу 120–800 Гц
- Плаваюча рама : Активне електромагнітне демпфування забезпечує зниження вібрації на 95%
- Адаптивні корпуси : Панелі змінної проникності забезпечують баланс між потоком повітря та контролем шуму
Польові випробування багатошарових систем ізоляції показали зниження випромінюваного шуму на 20–30 дБ при поєднанні мінеральної вати товщиною 100 мм із перфорованими алюмінієвими оболонками. Такий багатошаровий підхід відповідає рекомендованим ВООЗ граничним рівням шуму вночі (<45 дБА) для житлових зон.
Ключові технології зниження шуму в безшумних дизельних генераторах
Сучасні безшумні дизельні генератори інтегрують кілька інженерних рішень, щоб досягти рівнів шуму нижче 55 дБА на відстані 7 метрів — тишче, ніж у типових офісних приміщеннях. Ці технології враховують чотири основні типи шуму: механічний, від згоряння, вихлопний та вібраційний.
Сучасні акустичні корпуси та матеріали для звукоізоляції
Високоефективні композитні панелі з 2–3 шарами акустичної піни поглинають шум середніх частот (500–2000 Гц), тоді як вініл із підвищеною масою блокує низькочастотне гуркотіння двигуна. Атестація за ISO 3744 підтверджує, що ці корпуси зменшують повітряний шум на 30–45 дБ порівняно з відкритими конструкціями.
Системи глушіння вихлопу та технологія глушників
Багатокамерні рефлекторні глушники в поєднанні з скловолоконними абсорбційними трубками перетворюють хвилі тиску вихлопних газів на теплову енергію. Польові дослідження в міських умовах демонструють зниження рівня шуму на 20 дБ на критичних частотах 250–1000 Гц, які найбільше завдають шкоди слуху людини.
Антівібраційні кріплення та системи ізоляції
Ізолюючі елементи з неопренової гуми та гібридні опори з пружинним демпфуванням відокремлюють двигуни від рам, зменшуючи передачу структурного шуму на 89%у лікарняних установах. Це усуває поширене через підлогу «гуління», характерне для звичайних агрегатів.
Багатошарові бар’єри від шуму та композитні матеріали з демпфуванням
Перехресно-шаровані сталево-керамічні композити в стінах купола забезпечують на 50% вищу втрату звукопередачі (STL) порівняно з одношаровою сталью. Пористі керамічні гранули в передкамерах випуску додатково розсіюють шум згоряння за рахунок фазового пригнічення.
Інновації в конструкції надтихих генераторів для міського використання
Сучасні моделі оснащені активна відмова від шуму системи, що аналізують робочі гармоніки двигуна в режимі реального часу. У поєднанні з оптимізованими вентиляторами охолодження ці системи досягають 48–52 дБА рівнів шуму — у відповідності з найсуворішими нормами ЄС щодо шуму в житлових зонах. Незалежні випробування підтверджують, що ці конструкції відповідають стандартам ISO 8528 і зберігають повну номінальну потужність.
Реальна продуктивність за рівнем шуму: виміряні рівні дБ та практичні приклади
Середнє зниження рівня шуму: базовий рівень порівняно з приглушеним виходом
Сучасний тихі дизельні генератори забезпечують зниження шуму на 40–60% у порівнянні з традиційними моделями, як показано в 20-денному дослідженні, проведеному в 45 експлуатаційних сценаріях ( Дослідження журналу Nature ). Інтегровані системи приглушення, спрямовані на механічний, комбустійний та вихлопний шум, знижують базові рівні шуму з 85–90 дБА до 55–65 дБА під час безперервної роботи.
Типова продуктивність: <55 дБА на відстані 7 метрів у відповідних моделей
Пристрої, що відповідають міжнародним стандартам, таким як GB3096-2008, підтримують рівень шуму нижче 55 дБА на відстані 7 метрів — що еквівалентно помірному дощу. Для порівняння:
| Сценарій | Рівень шуму | Відстань |
|---|---|---|
| Міський денний стандарт | ≈55 дБА | 7 метрів |
| Традиційний генератор | 78–85 дБА | 7 метрів |
Дослідження випадку: встановлення в лікарнях та житлових зонах
У проєкті 2023 року у сфері охорони здоров’я із застосуванням приглушених генераторів було зафіксовано:
- 58 дБА у внутрішніх дворах лікарні (на відміну від 82 дБА для неприглушених резервних джерел)
-
53 дБА на межі житлових територій під час нічних відключень
Ці результати відповідають рекомендованим ВООЗ пороговим значенням для чутливих середовищ.
Польові дані щодо міських розгортань супертихих дизельних генераторів
Останні розгортання в метрополітені показують, що приглушені генератори зменшують шумове забруднення в мікрорайонах на 34%під час відключень електропостачання. Акустичне картування підтверджує відповідність суворим постановам, наприклад, нічному обмеженню 50 дБА в Нью-Йорку, коли встановлено спрямовані глушники вихлопних газів.
Тихі та традиційні дизельні генератори: порівняння рівня шуму
Кількісний аналіз: рівень шуму в традиційних та тихих моделях
Тихі дизельні генератори забезпечують на 40–60% нижчий рівень шуму, ніж традиційні моделі, працюючи в межах 55–75 дБА проти 85–110 дБА . Ця різниця має важливе значення в міських районах, де норми щодо шуму часто обмежують рівень приблизно до 75 дБА.
| Метричні | Тихі дизельні генератори | Традиційні генератори |
|---|---|---|
| Середній рівень шуму | 62–68 дBA | 92–98 дBA |
| Пікова частота | 125–250 Гц | 500–1 000 Гц |
| Вплив відстані користувача | компліантний радіус 7 м | на відстані 25 м та більше — створює завади |
Джерело: Товариство промислової акустики (2023), стандартизовані вимірювання на відстані 7 метрів
Акустичний слід у відкритих та закритих середовищах
Конструкція традиційних генераторів із відкритою рамою дозволяє 360° розсіювання шуму , збільшуючи їх акустичний слід на 30% у міських каньйонах. Безшумні моделі використовують композитні корпуси, які поглиначають 92% механічного та вихлопного шуму всередині, обмежуючи поширення за межами до радіуса 12 метрів порівняно з понад 40 метрами для незахищених пристроїв.
Сприйняття комфорту користувачем та експлуатаційні переваги
На рівні 65 дБА — порівняно з приглушеним шумом пральної машини — безшумні дизельні генератори дозволяють спілкуватися особисто (<3 м) без підвищення голосу. Традиційні пристрої перевищують 85 дБА, що відповідає рівню шуму сміттєвоза, і вимагають засобів захисту слуху під час тривалого впливу. Лікарні, які використовують безшумні моделі, повідомляють про на 72% менше скарг, пов’язаних із шумом (Інститут міського здоров’я, 2022).
Ефективність готових звукоізоляційних корпусів у містах
Модульні акустичні корпуси зменшують шум генераторів у містах на 18–22 дБА завдяки:
- Трьохшарова оцинкована сталь зі шаром мінеральної вати (блокує 97% частот понад 500 Гц)
- Рами з демпфуванням вібрацій (на 85% зменшує шум, що передається конструкцією)
- Похилі витяжні отвори з багатшторовою технологією
Ці системи дозволяють 89% опитаних міст дотримуватися норм шуму вночі без компромісу щодо часу роботи чи доступу до обслуговування
Відповідність вимогам щодо шуму та галузевим стандартам
Огляд глобальних та місцевих норм щодо шуму для генераторів
Дизельні генератори, що працюють тихо, повинні дотримуватися суворих правил залежно від місця встановлення. У Європі існує Директива ЄС щодо шумового забруднення довкілля, яка фактично зобов'язує компанії постійно контролювати рівень шуму своїх машин. Також існує стандарт ISO 1996-2:2017, який чітко визначає, як правильно вимірювати рівні шуму в навколишньому середовищі. Ситуація схожа і за океаном. Наприклад, у провінції Онтаріо місцеві органи влади вимагають проведення перевірок шуму в межах 30 метрів від будь-якого місця встановлення. У всьому світі більшість виробників прагне до значення нижче 55 децибел (А-зважених) при вимірюванні на відстані семи метрів від агрегату. Це число є досить важливим, оскільки воно визначає, чи можуть ці генератори використовуватися поблизу житлових будинків без отримання скарг. Аналіз регулювання шумового забруднення в різних регіонах світу показує, що насправді існує зростаюча згода щодо того, що вважається прийнятним рівнем тиші для дизельних генераторів.
Відповідність міським нормам щодо шуму: досягнення межі <55 дБА
Тихі генератори, розроблені для сучасних міст, використовують передові інженерні рішення, щоб вписатися в урбаністичний простір. Останні моделі оснащені сучасними системами глушників, які зменшують рівень шуму від вихлопу приблизно на 15–20 децибел, а їх композитні корпуси ефективно запобігають неприємним механічним вібраціям. Практичні випробування в лікарнях показали, що ці пристрої зберігають стабільний рівень шуму на позначці 52–54 децибели, навіть коли працюють на повну потужність у години пік, що відповідає стандартам EPA для тихої роботи вночі. Однак найважливішим є те, наскільки добре вони подавляють певні частоти. Більшість людей вважають особливо неприємними звуки у діапазоні приблизно від 63 Гц до 1 кГц, тому виробники приділяють особливу увагу ізоляції саме цього діапазону, у якому людське вухо є найчутливішим.
Чи всі 'тихі' позначки дійсно відповідають вимогам? Критичний аналіз
Термін «безшумний генератор» може вводити в оману, оскільки багато моделей насправді не відповідають заявленим характеристикам. Незалежні тести виявили різницю близько 8 децибел у деяких агрегатах, які виробники позиціонують як відповідні нормам. Під час вибору звертайте увагу на машини, які сертифіковані за стандартом ISO 3744, оскільки це означає, що вимірювання рівня шуму проводилося незалежною від компанії стороною. Виробники, які дотримуються рекомендацій ANSI S12.9-2014, зазвичай надають точніші показники при експлуатації в реальних умовах. Це має велике значення, якщо обладнання використовується в місцях, де діють норми щодо рівня шуму, адже неточні вимірювання можуть призвести до дорогих проблем із дотриманням вимог у майбутньому.
Часто задані питання
Що робить дизельні генератори безшумними?
Безшумні дизельні генератори використовують передовий акустичний дизайн, спеціальні корпуси та ізоляцію від вібрацій для мінімізації рівня шуму.
Наскільки ефективні звукоізоляційні корпуси для дизельних генераторів?
Звукоізоляційні корпуси можуть знизити повітряний шум на 30–45 дБ залежно від конструкції та матеріалів.
Чи відповідають тихі генератори нормам з шуму?
Багато тихих генераторів відповідають нормам з шуму, якщо вони належним чином сертифіковані за стандартами, наприклад ISO 3744.
Як співвідносяться тихі генератори з традиційними моделями за рівнем шуму?
Тихі генератори, як правило, працюють на рівні 55–75 дБА, що значно нижче, ніж у традиційних моделей, які можуть перевищувати 85 дБА.
Зміст
- Розуміння основних принципів тихої роботи дизельного генератора
- Ключові технології зниження шуму в безшумних дизельних генераторах
- Реальна продуктивність за рівнем шуму: виміряні рівні дБ та практичні приклади
- Тихі та традиційні дизельні генератори: порівняння рівня шуму
- Відповідність вимогам щодо шуму та галузевим стандартам
- Часто задані питання